Health
Extreme heatwaves Delhi: Five health risks associated with temperatures exceeding 45 degrees

A severe heatwave that reached 45–47 degrees in several areas of North India, including Delhi, has made it crucial to take precautions against heat exposure in order to prevent heatstroke, dehydration, and other heat-related ailments. Elevated body temperatures can cause severe harm to the brain, heart, kidneys, and other organs, as well as other chronic problems. It is imperative that you stay indoors during the hottest parts of the day and stay well-hydrated by drinking lots of water, as well as fruits, vegetables, buttermilk, nimbu paani, and coconut water.
The body’s natural capacity to regulate temperature may be severely compromised above 45 degrees or higher, which can result in disorders like heat stroke, which can cause fever, disorientation, dizziness, or seizures. Extended exposure to high temperatures might potentially harm vital organs such as the heart, brain, and other tissues. If proper measures are not taken to cool the body down, it may potentially be deadly.
According to Dr. Tushar Tayal, Consultant in Internal Medicine at CK Birla Hospital in Gurugram, exposure to outside temperatures more than 45°C (113°F) can have detrimental, even fatal, impacts on human health.
Heat stroke can result from the body’s inability to control its internal temperature at such high temperatures. High body temperature (over 40°C or 104°F), disorientation, unconsciousness, and occasionally convulsions are among the symptoms. Heat stroke can be fatal if medical attention is not received right away. Severe dehydration results from the body losing fluids quickly through perspiration in an effort to cool down. According to the specialist, “this can result in symptoms like intense thirst, dry mouth, decreased urine production, and in severe cases, confusion, dizziness, and fainting.”
Unsettling consequences of the heatwave
Dr. Tayal lists further negative consequences of being in a severe heatwave:
Damage to the brain and heart: Hyperthermia, or dangerously elevated body temperature, can be brought on by extended exposure to intense heat. If left untreated, this illness can harm the muscles, heart, brain, kidneys, and kidneys, which can result in long-term health problems or even death.
Extended exposure to high temperatures can result in heat exhaustion, a milder type of heat-related disease. Severe perspiration, weakness, headache, nausea, dizziness, and cramping in the muscles are some of the symptoms. It can develop into heat stroke if left untreated.
Skin damage: High temperatures can lead to serious skin damage, such as sunburn and, in severe cases, second-degree burns, especially when accompanied with bright sunshine. Long-term exposure to UV radiation can also raise the chance of developing skin cancer.
cites the following five important health impacts of temperatures rising beyond 45 degrees:
1. Heat stroke and exhaustion
The body finds it difficult to regulate its temperature when it is exposed to high temperatures over prolonged periods of time. Heat exhaustion may result from this, which is characterised by symptoms including headaches, nausea, dizziness, and profuse perspiration. Heat exhaustion can develop into heat stroke, a potentially fatal illness when the body’s ability to regulate its temperature fails, if it is not treated quickly. Heat stroke is characterised by a high body temperature (over 40 degrees Celsius), disorientation, a fast heartbeat, and unconsciousness. Getting medical help right away is essential to avoiding fatalities or major problems.
2. Lack of fluids
The body quickly loses water through perspiration when it is really hot, trying to cool down. Insufficient consumption of fluids may result in dehydration. When the body loses more fluids than it takes in, it becomes dehydrated and can’t perform its regular tasks. Dehydration symptoms include weariness, dizziness, dark urine, dry mouth, and decreased urination. Electrolyte abnormalities, shock, and renal damage can result from severe dehydration.
3. Stress on the heart
Elevated body temperature exerts additional strain on the cardiovascular system. Blood arteries dilate (expand) to remove heat, and the heart beats harder to pump more blood to the skin’s surface. This increased effort raises the risk of heart attacks and strokes and can worsen pre-existing cardiac problems. Extreme heat events put older people, those with cardiovascular disease, and people with hypertension at risk.
4. Issues with breathing
Because ground-level ozone and other pollutants are more concentrated in warm weather, the quality of the air might deteriorate. The combination of high temperatures and poor air quality can worsen respiratory ailments including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Additionally, heat encourages the spread of allergens and particulate particles, which worsens respiratory conditions.
5. Skin issues and heat rash
Heat rash, which is characterised by sweating and prolonged exposure to high temperatures, can result in swollen and clogged sweat ducts, which can produce pain and itchy red lumps on the skin. Furthermore, too much sun exposure raises the possibility of being sunburned, which damages skin and raises the chance of developing skin cancer. In periods of intense heat, wearing adequate clothes and sunscreen is vital to protecting the skin.
Preventative actions
To lessen the damaging effects of intense heat on health
Keep yourself hydrated by drinking a lot of water all day long, even if you don’t feel thirsty. Steer clear of coffee and alcohol since they might dehydrate the body.
Keep cool by spending time in air-conditioned spaces throughout the hottest parts of the day. Take cold showers, use fans, and dress in airy, loose-fitting clothing.
Minimise outdoor activity: Steer clear of vigorous activities, especially during the warmest times of the day. If you must go outside, make sure to drink plenty of water and take frequent rests in the shade.
Keep an eye on those who are susceptible: Due to their increased vulnerability to heat-related diseases, keep a watch on the elderly, young children, and individuals with ongoing medical issues.
Use sunscreen: To shield your skin from damaging UV rays, slather on a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF.
Being aware of the rising temperatures and being prepared are essential to avoiding health problems associated to heat. Keep yourself and your loved ones safe from the risks of severe heat by keeping up with weather predictions and heat advisories and by taking preventative measures.
General News Platform – https://ihtlive.com/
Entertainment News Platforms – anyflix.in
Construction Infrastructure and Mining News Platform – https://cimreviews.com/
Podcast Platforms – https://anyfm.in/
COVID-19
How prompt care and basic precautions can help keep high-risk people safe during the COVID-19 outbreak

According to Dr. Viny Kantroo, senior consultant at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals in Delhi, people in high-risk groups, such as diabetics and pregnant women, must behave in a way that is appropriate for COVID-19.
Experts have warned that high-risk groups, such as those over 65 and those with comorbidities including diabetes, chronic lung or kidney illness, and cardiac diseases, should exercise extreme caution in light of the increased number of COVID-19 cases and deaths.
For these individuals, COVID-appropriate behavior is crucial, according to Dr. Viny Kantroo, senior consultant in respiratory, critical care, and sleep medicine at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals in Delhi.
This includes avoiding touching your face, keeping your hands clean, controlling chronic conditions like diabetes to prevent complications, wearing a mask in crowded areas, when traveling, or if you have respiratory symptoms, and practicing respiratory etiquette, such as coughing or sneezing into a tissue or your elbow.
With 4,866 ongoing infections and seven recent deaths—including the death of a five-month-old baby with cerebral palsy—India is seeing a new surge in coronavirus infections. Medical specialists emphasize that the present varieties produce milder sickness in most people, even though the spike is worthy of notice.
According to Dr. Kantroo, knowledge, adherence to COVID-appropriate behavior, and prompt care for vulnerable populations are crucial for navigating this period.
There are currently 28–30 patients in Delhi’s hospitals, and the majority of admissions are either preventative or involve high-risk patients. The majority of infections are still mild or moderate, and the medical system is equipped to deal with these situations.
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication, such as Paxlovid, for patients with high-risk conditions who test positive, preferably within five days of the onset of symptoms and after evaluating liver and kidney function.
Complications are still most likely to affect high-risk groups. If you fit into any of the following categories, you should be extra watchful:
- Senior citizens (those over 65)
- People with heart, lung, renal, or liver illness as well as diabetics
- People with impaired immune systems, such as those receiving steroids or immunosuppressants, cancer patients, and transplant recipients
- Women with comorbidities who are pregnant
- Individuals who have previously had a serious COVID infection
- Seek prompt medical attention if you suffer from:
- Breathlessness
- Low saturation of oxygen
- Symptoms that last longer than seven days
- A fever that is not getting better with medicine.
Do we require a follow-up vaccination? In India, booster vaccinations are currently not advised for the general public. Authorities such as the World Health Organization (WHO) are still evaluating the virus’s changing behavior, and there are currently no new COVID-19 boosters accessible locally. Nonetheless, the emphasis should continue to be on general health, masking, and early diagnosis; high-risk patients should speak with their doctors about preventative care.
New Omicron sub-variants including JN.1, NB.1.8.1, LF.7, and XFC, which have demonstrated greater transmissibility but only minor symptoms, are responsible for the present spike. These are now categorized by the WHO as “Variants Under Monitoring”—not yet concerning, but needing vigilance. Like influenza, these viruses are known to evolve, which is why seasonal updates and monitoring are still important.
According to Dr. Kantroo, the current COVID-19 phase calls for prudence, readiness, and responsible behavior rather than panic. We can keep ourselves and our communities safe by taking simple precautions, remaining informed, and getting care when we need it.
Prompt care and basic precautions are vital in safeguarding high-risk individuals during the COVID-19 outbreak. High-risk groups include older adults (especially those over 65), individuals with underlying health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, chronic lung disease, obesity, or weakened immune systems, and pregnant women.
One of the most effective strategies is staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccinations, including recommended booster doses. Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
Practicing good hygiene is essential. Regularly washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer when soap is unavailable, helps eliminate germs. Avoid touching the face, particularly the eyes, nose, and mouth, with unwashed hands.
Wearing masks in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor spaces adds a layer of protection, especially for those at higher risk. Masks help prevent the inhalation of respiratory droplets that may contain the virus.
Maintaining physical distance from others, particularly in public settings, reduces the chance of exposure. Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick is also crucial.
Ensuring proper ventilation in indoor spaces by opening windows and doors or using air filtration systems can decrease the concentration of airborne virus particles.
High-risk individuals should consult healthcare providers promptly if they exhibit COVID-19 symptoms. Early medical intervention can lead to timely treatment, which is more effective when started soon after symptom onset.
Staying informed about local COVID-19 trends and following public health guidelines helps individuals make informed decisions about attending events or traveling. In areas with high transmission rates, extra precautions are warranted.
By adhering to these basic precautions and seeking prompt medical care when necessary, high-risk individuals can significantly reduce their risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19.
During the COVID-19 outbreak, high-risk individuals such as the elderly, those with chronic illnesses, immunocompromised patients, and pregnant women require an extra layer of protection through timely care and consistent preventive measures.
Prompt medical attention at the earliest sign of symptoms can drastically reduce the severity of the infection, allowing for early intervention strategies like antiviral medication or supportive treatment before complications escalate. This proactive approach can be life-saving, especially for those with compromised immunity or pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
In tandem with early care, basic daily precautions form a critical defense line. Regular handwashing with soap not only removes viruses from the skin but also limits the transmission of the virus to surfaces and other people. Wearing masks in indoor or crowded settings, especially where physical distancing isn’t possible, reduces the risk of inhaling infectious particles. For high-risk individuals, this precaution is not optional but essential, especially in community spread environments.
Physical distancing remains one of the most effective non-medical tools for protecting vulnerable populations. Avoiding unnecessary social gatherings, maintaining at least six feet of space in public, and opting for virtual interactions instead of face-to-face meetings can dramatically lower exposure risks. Meanwhile, ensuring good airflow in living spaces—either by opening windows or using air purifiers—dilutes potential airborne contaminants, making the environment safer.
Vaccination, including booster doses, remains the cornerstone of protection. For high-risk people, being fully vaccinated not only prevents severe disease but also lowers the chances of hospitalization and long-term complications. In households with vulnerable members, ensuring that all residents and caregivers are vaccinated creates a collective shield that reduces viral transmission within shared spaces.
Monitoring health indicators regularly, such as body temperature, oxygen saturation levels, and symptoms like persistent cough or breathlessness, can provide early warning signs. A delay in seeking help can turn a manageable illness into a life-threatening emergency. Therefore, having access to telemedicine services or regular check-ins with healthcare professionals can bridge this gap and offer timely guidance.
Moreover, high-risk individuals benefit from a well-prepared routine. Keeping a stock of essential medications, arranging emergency contacts, and having a ready plan for isolation or hospitalization if symptoms appear can ease the mental and physical toll. Emotional support is equally important—social isolation can lead to depression, which weakens immunity. Regular phone calls, virtual meetups, or socially-distanced interactions with loved ones help maintain a positive outlook and mental strength.
Overall, protecting high-risk individuals isn’t just about reacting to illness—it’s about creating a daily environment of safety, vigilance, and care. These combined efforts don’t just reduce risk—they provide peace of mind and resilience in the face of uncertainty.
Early recognition of symptoms like fever, fatigue, cough, or shortness of breath can make a critical difference for high-risk individuals. Rather than waiting for symptoms to intensify, acting immediately by consulting a healthcare provider enables timely medical evaluation. This early detection can help determine whether home care is sufficient or if hospitalization may be required to prevent deterioration. When action is delayed, especially among elderly patients or those with diabetes or heart disease, the virus can progress rapidly, leading to avoidable complications.
Nutrition also plays a crucial role in building and maintaining a strong immune response. High-risk individuals should focus on a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, such as Vitamin C, D, zinc, and iron. These nutrients help enhance immune defense mechanisms, improve respiratory function, and reduce inflammation. Staying hydrated, avoiding processed foods, and managing blood sugar levels are daily steps that can significantly reduce the body’s vulnerability to viral infection.
Stress management is another essential factor in preserving health during a pandemic. Constant news updates and fear of infection can increase anxiety, especially in those already dealing with health challenges. Chronic stress has been proven to weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. High-risk individuals can benefit from relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or gentle walks in open, low-traffic spaces. Creating a calm and reassuring environment at home also helps lower overall stress levels.
Ensuring regular sleep of 7–8 hours each night is another natural shield against illness. Sleep strengthens the immune response and supports the body in fighting infections more effectively. High-risk individuals should maintain a consistent sleep schedule, limit caffeine and screen time before bed, and create a comfortable, well-ventilated sleeping environment. Lack of sleep, on the other hand, can increase the body’s inflammatory response and reduce its ability to respond to viral threats.
Communication is vital, especially when a high-risk person lives alone or has limited mobility. Maintaining a clear line of contact with caregivers, family members, or community support groups ensures that help is available if symptoms arise or essential supplies run out. Establishing a daily or weekly check-in system, whether through phone calls, text messages, or video chats, helps keep vulnerable individuals connected and monitored.
Medication adherence is another pillar of health management. People with chronic conditions like hypertension, COPD, or kidney disease must continue taking their prescribed medications without interruption. Stocking at least two weeks’ worth of essential medicines, using pill organizers, and setting reminders can help prevent missed doses. Missing treatment for pre-existing conditions can weaken the body and complicate recovery from COVID-19 if infection occurs.
In multi-generational households, where older adults often live with younger family members, it’s important for everyone to adopt preventive behaviors. Children and young adults may be asymptomatic carriers, so wearing masks indoors when someone is sick, regularly sanitizing surfaces, and minimizing outside contact when not essential are critical practices to prevent internal household transmission.
Sanitization protocols inside the home should be followed consistently. Frequently touched surfaces—such as door handles, light switches, mobile phones, and remote controls—should be cleaned daily using alcohol-based or bleach-based disinfectants. Maintaining hand hygiene before meals, after returning from outside, or after coughing or sneezing remains a simple but highly effective tool to reduce risk.
In the case of caregivers visiting high-risk individuals, strict hygiene measures should be followed. They should wear masks, sanitize hands before entering the premises, and avoid close contact if they are feeling unwell. Caregivers should also limit their own exposure outside to reduce the risk of becoming carriers of the virus. The safety of a high-risk person is often dependent on the behavior of those around them.
Public transportation and crowded places present a serious threat to high-risk individuals. If travel is unavoidable, choosing off-peak hours, maintaining distance, wearing high-filtration masks like N95 or KN95, and minimizing surface contact are recommended strategies. Whenever possible, using private or sanitized transport options can further lower exposure risks.
- Group Media Publication
- Construction, Infrastructure and Mining
- General News Platforms – IHTLive.com
- Entertainment News Platforms – https://anyflix.in/
Q1. What are the most effective ways to protect high-risk individuals at home?
Ensure regular handwashing, mask usage, physical distancing from visitors, well-ventilated rooms, vaccination, and daily health monitoring. Limit non-essential exposure and sanitize frequently-touched surfaces.
Q2. Should high-risk people avoid hospital visits completely?
Not necessarily. Routine or emergency visits should not be avoided if needed. However, telemedicine consultations should be prioritized for non-urgent issues, and all safety protocols should be followed for in-person visits.
Q3. How can caregivers ensure they don’t transmit COVID-19 to vulnerable people?
Caregivers should follow strict hygiene, wear masks, monitor their own health, get vaccinated, avoid exposure to crowded places, and immediately isolate if they show symptoms.
Q4. How can I keep my elderly parents informed without creating panic?
Share verified, simple information calmly. Focus on positive actions they can take (like safety habits) and avoid exposing them to constant negative news or misinformation.
Q5. Is it safe for high-risk individuals to attend social events if cases decline?
Caution is still advised. Even if cases decline, high-risk individuals should avoid crowded indoor events, wear high-filtration masks if attending essential gatherings, and maintain distancing.
India
Covid 19 India Cases Live Updates: Active cases rise to nearly 5,000, 7 deaths reported in 24 hours
.jpg)
State-wise Breakdown
Kerala remains the most affected state, with 1,487 active cases. Delhi and Maharashtra follow, reporting 562 and 526 active cases respectively . Other states such as Gujarat, Karnataka, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh have also seen noticeable increases in active cases.
Emerging Variants and Diagnostic Challenges
The resurgence is partly attributed to new variants, notably NB.1.8.1, which exhibit higher transmissibility. These variants often present with milder symptoms resembling common colds or flu, such as low-grade fever, fatigue, and cough. This similarity complicates timely diagnosis and may lead to underreporting .
Government Response and Public Health Measures
In response to the uptick in cases, health authorities have conducted review meetings and directed states to ensure readiness with essential supplies. The public is urged to maintain hygiene and seek medical attention if experiencing respiratory symptoms as the ministry closely monitors the situation .
Public Advisory
Health experts advise the public to remain vigilant. Individuals experiencing symptoms such as fever, cough, or fatigue should seek medical advice promptly. High-risk groups, including the elderly and those with underlying health conditions, are particularly encouraged to take preventive measures.
India is once again witnessing a slow but worrying uptick in COVID-19 cases, prompting health experts and officials to revisit pandemic protocols that had largely faded from public memory. As per the latest data released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the number of active COVID-19 cases in the country has climbed to approximately 4,866, marking a noticeable increase over the past few days. In the preceding 24-hour period alone, India reported 564 new cases and seven deaths attributed to COVID-related complications.
Among the deceased is a five-month-old infant, serving as a grim reminder that the virus remains dangerous across all age groups. While this resurgence is nowhere near the peak levels seen during the Delta or Omicron waves, the rapid climb from under 2,000 active cases just weeks ago has raised concerns about a potential localized outbreak or seasonal spread. Kerala, which has historically experienced higher caseloads during previous waves, currently tops the chart with nearly 1,487 active cases.
Delhi follows with 562 cases, and Maharashtra stands close behind at 526, indicating that urban and densely populated regions continue to be hotspots. Other states such as Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, West Bengal, Gujarat, and Uttar Pradesh are also reporting a steady rise in daily case counts, although they remain under the 500 mark.
What adds complexity to the current situation is the emergence of new sub-variants, notably NB.1.8.1, which appear to be driving the present surge. Unlike earlier strains, this sub-variant is said to spread faster but often manifests in symptoms that mimic those of seasonal flu — such as low-grade fever, dry cough, fatigue, and occasional sore throat — making detection difficult without targeted testing.
In many cases, infected individuals initially assume they are suffering from the common cold or seasonal allergies and delay seeking medical care, increasing the risk of community transmission. Doctors across hospitals in metro cities have reported that several patients only test positive for COVID after secondary or tertiary symptoms emerge, often resulting in a lag in treatment and isolation measures.
This diagnostic challenge is also contributing to underreporting, as people shy away from testing unless symptoms become severe. Experts warn that such complacency could lead to undetected clusters and recommend that anyone experiencing prolonged flu-like symptoms undergo testing, particularly those with underlying health conditions or weakened immunity.
In response to the rising case numbers, the Indian government has begun taking precautionary steps. Union Health Minister-led review meetings have been conducted to assess state-level preparedness.
Hospitals have been instructed to stock up on essential supplies, including PPE kits, oxygen cylinders, antiviral medication, and to ensure that ICU beds and isolation wards are functional. States have been directed to revive COVID war rooms and surveillance systems temporarily, especially in high-risk zones and transportation hubs.
District health officials in Kerala and Maharashtra have already reinstated mobile testing vans in public places like railway stations, airports, and markets to ensure early identification of potential cases.
However, authorities are treading a careful line, avoiding full-blown restrictions to prevent public panic or economic disruption, and instead focusing on enhanced monitoring and communication.
Public health advisories have also been updated. Citizens are encouraged to practice respiratory hygiene, such as wearing masks in crowded indoor spaces, regularly sanitizing hands, and maintaining physical distancing wherever feasible.
Those experiencing flu-like symptoms are advised to avoid public gatherings and seek medical consultation at the earliest. Booster vaccinations, although no longer mandatory, are being strongly recommended for vulnerable populations — including senior citizens, people with comorbidities, and frontline workers. While vaccination rates in India remain high, especially in urban centres, health authorities are now encouraging states to initiate local awareness drives to encourage booster uptake, particularly in semi-urban and rural regions.
Recent genome sequencing reports suggest that while the current strain does not lead to severe hospitalization in most healthy individuals, patients with coexisting illnesses — such as diabetes, respiratory diseases, or cardiac conditions — may face higher risks, necessitating timely intervention.
Educational institutions and offices have been advised to remain alert and monitor the health of students and staff. So far, no decisions have been made regarding closures or reverting to remote operations. However, many IT companies have begun recommending hybrid work setups once again, especially for employees showing even mild symptoms of illness.
In schools and colleges, periodic screening and health monitoring initiatives have been reintroduced. Several private hospitals in Bengaluru, Chennai, and Mumbai have reported a modest increase in the number of walk-in patients requesting COVID tests over the past week — a sign that public awareness is gradually rising. However, experts caution that proactive measures must continue if the country is to avoid a repeat of past surges.
Adding to the complexity is the simultaneous occurrence of seasonal flu outbreaks in several parts of the country, particularly in North India, where weather fluctuations are common during this time of year. Many doctors are finding it difficult to distinguish between influenza and COVID-19 without proper diagnostic tests, further burdening healthcare infrastructure.
Although hospitalizations remain relatively low, the medical community is urging people not to take the current wave lightly. They emphasize that a small percentage of infections can still evolve into serious respiratory complications requiring hospital admission, especially if diagnosis or treatment is delayed.
Public sentiment, meanwhile, remains mixed. After enduring multiple lockdowns and disruptions since 2020, many citizens are understandably fatigued by the reappearance of COVID-related headlines. While some have returned to mask-wearing and hand hygiene habits, others continue to treat the situation casually, attributing symptoms to routine flu or dust allergies. This divide poses a challenge for public health messaging, which needs to strike a balance between awareness and alarm. Social media platforms are also being monitored to curb the spread of misinformation and fake remedies that tend to gain traction during health emergencies.
In conclusion, while the number of active COVID-19 cases in India remains well below critical thresholds, the recent spike underscores the virus’s continued presence and adaptability. The emergence of new variants, combined with milder symptoms and reduced public vigilance, creates a fertile ground for future flare-ups.
Government agencies, healthcare professionals, and citizens must now work together to ensure that India’s hard-earned progress in pandemic management is not undermined by complacency. With schools open, festivals around the corner, and increased travel across the country, it is imperative that basic precautions be maintained. Timely diagnosis, voluntary isolation, mask usage, and booster vaccination are simple yet powerful tools that can help India prevent another wave from escalating into a crisis.
- Group Media Publication
- Construction, Infrastructure and Mining
- General News Platforms – IHTLive.com
- Entertainment News Platforms – https://anyflix.in/
Health
In a lavender Manish Malhotra saree, Hania Aamir sports her most gorgeous ethnic ensemble to date. View its astounding cost.

Hania Aamir serves stunning ethnic fashion inspiration in lavender Manish Malhotra tissue saree. Wondering how much it costs? Scroll down for all the details.
Hania Aamir is leaving fashion lovers spellbound with her stunning ethnic diaries. The Pakistani actor has been rocking back-to-back traditional outfits by Indian designers, turning her Insta feed into a goldmine of fashion inspo. For her latest look, the 27-year-old slipped into six yards of grace and looked straight out of a royal fairytale. Let’s break down her saree look and steal some style tips for your ethnic wardrobe. Hania Aamir stuns in lavender saree
On Monday, Hania took to Instagram and uploaded a series of gorgeous snaps accompanied by the caption “gave mermaid.” Draped in a dreamy lavender saree, the star looked absolutely breathtaking while serving some striking glam poses. Let’s take a moment to soak in her ethereal beauty.
Hania’s saree is crafted from luxurious tissue fabric and features intricately embroidered borders, showcasing stunning zari work, beads, and sequin detailing throughout. Draped to perfection, she let the pallu elegantly cascade from her shoulder, adding a regal charm to her look. She teamed it up with a matching embroidered blouse, complete with delicate handmade tassels at the back.
How much does her saree cost?
Can’t stop swooning over Hania’s gorgeous saree? We’ve got all the details you need to add this stunner to your collection. Her six yards is straight from the shelves of ace designer Manish Malhotra and is priced at ₹3,95,000.
Hania accessorised her ethnic look with dazzling diamond jewellery, including statement drop earrings, a chic choker necklace, a sleek bracelet, and a stunning ring adorning her finger. Her dewy makeup featured shimmer eyeshadow, winged eyeliner, mascara-coated lashes, blushed cheeks, a luminous highlighter, and glossy nude lipstick. With her long, luscious tresses left loose in a side partition, she perfectly finished off her look.
Group Media Publications
Entertainment News Platforms – anyflix.in
Construction Infrastructure and Mining News Platform – https://cimreviews.com/
General News Platform – https://ihtlive.com/
-
Tech5 months ago
Best Zebronics Bluetooth speakers you can buy today for an unmatched audio experience
-

 India2 years ago
India2 years agoNew Season 8 The Walking Dead trailer flashes forward in time
-

 India2 years ago
India2 years agoThe afternoon briefing revealed that 97.26% of the ₹2000 notes were returned, and the Israeli Prime Minister committed to war goals.
-
 World1 year ago
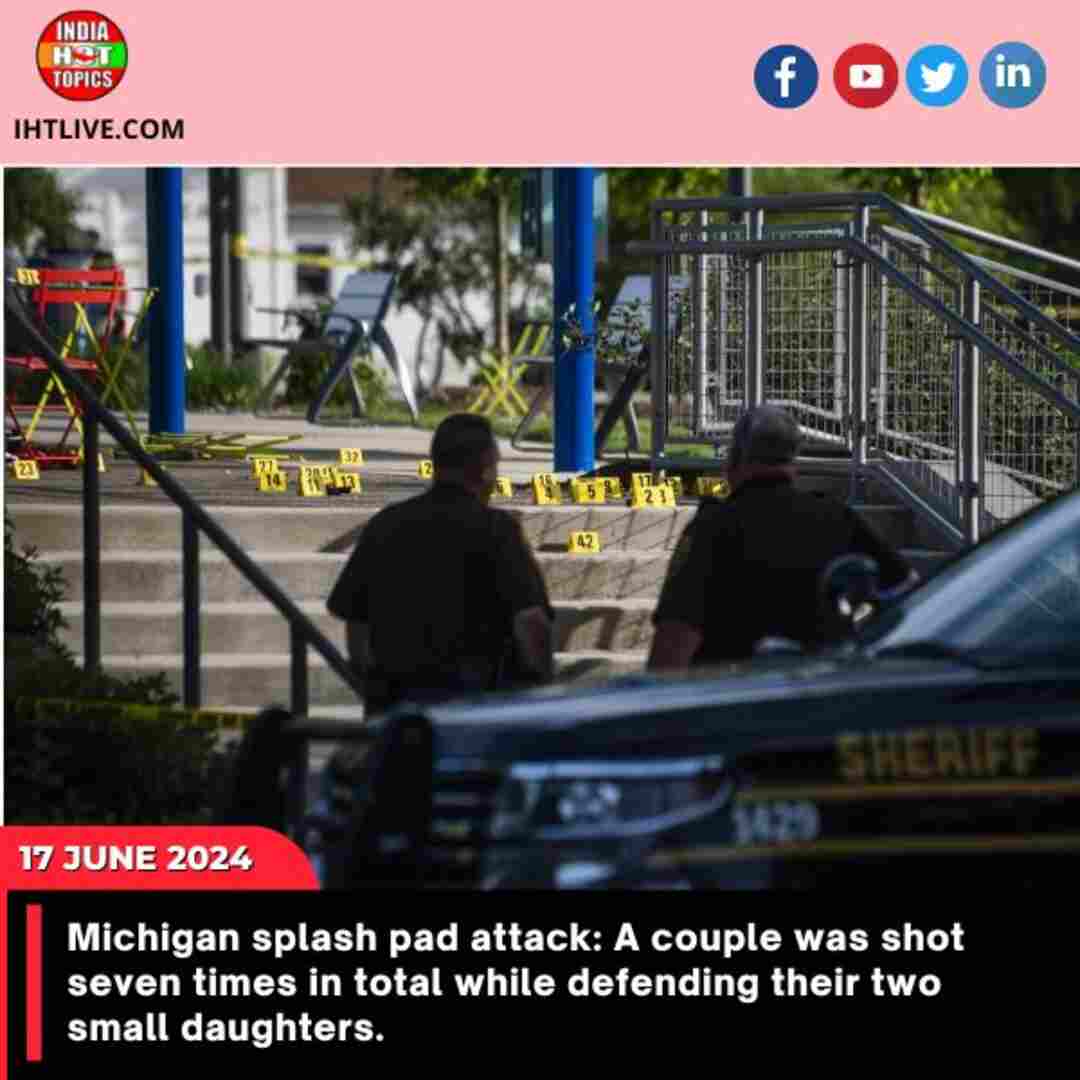
World1 year agoMichigan splash pad attack: A couple was shot seven times in total while defending their two small daughters.
-
 India2 years ago
India2 years agoSrikanth Venkatachari is appointed as the new chief financial officer by Reliance Industries.
-

 India2 years ago
India2 years agoPM Modi’s Three-Nation Tour Begins with a Traditional Welcome in Papua New Guinea
-
 Special 365 days3 years ago
Special 365 days3 years agoFlag Day of India
-

 India8 years ago
India8 years agoThe 9 worst mistakes you can ever make at work









.jpg)
.jpg)
%20(1).jpg)